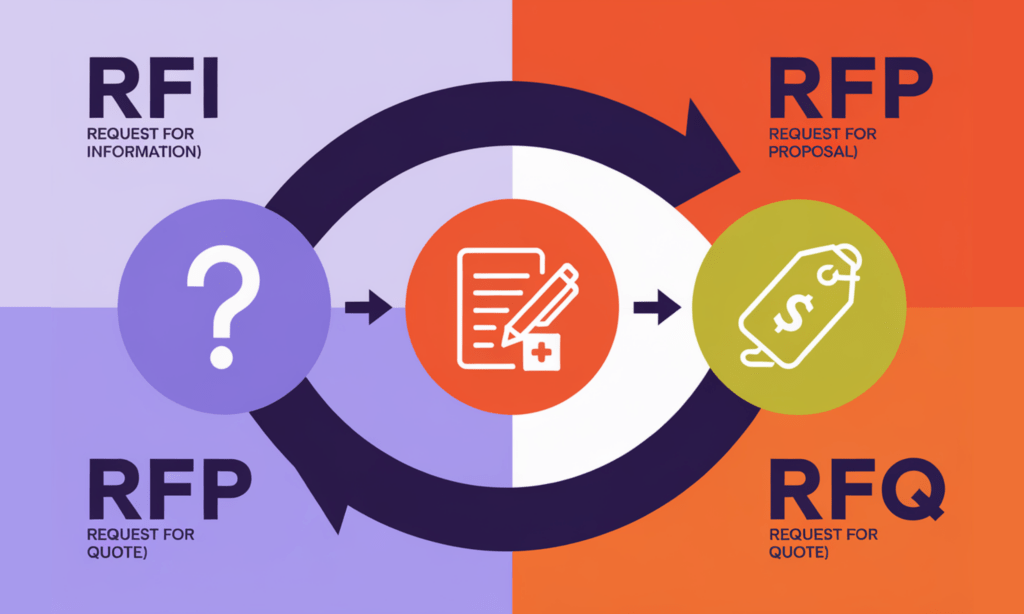
RFI, RFP, and RFQ are key components in the procurement process. These documents are pivotal for strategic sourcing and evaluating vendors. Yet, many procurement teams find it challenging to discern their differences.
Understanding each request type will enhance your sourcing workflow, help you negotiate better prices, and foster robust supplier relationships.
In this article, we’ll explore RFx documents, their unique features, best practices for implementation, and their role in procurement orchestration.
Whether you’re an experienced procurement expert or a novice, grasping the significance of RFI, RFQ, and RFP will empower you to enhance value, reduce risks, and fulfill your strategic sourcing objectives.
Key Takeaways
- RFI, RFP, and RFQ serve distinct purposes in the procurement process
- Mastering RFx documents is crucial for effective strategic sourcing
- RFI gathers information, RFP seeks proposals, and RFQ requests specific pricing
- Leveraging technology streamlines RFx management and procurement orchestration
- Understanding RFx best practices drives value and mitigates risks in sourcing
Understanding the Procurement Process
Let’s take a look at the meaning and use of each of these steps. RFI (Request for Information), RFP (Request for Proposal), and RFQ (Request for Quotation) are integral to a procurement strategy’s success. Each document has a distinct role at various stages of the procurement process, which is typically used to collect essential information, assess potential suppliers, and select the ideal vendor for your organization’s requirements.
- RFQ (Request for Quotation) focuses on obtaining cost estimates for predefined elements.
- RFP (Request for Proposal) involves soliciting detailed proposals from vendors to address a specific business need.
- RFI (Request for Information) is used to gather information about the capabilities of various vendors and their products/services.
Orchestrating these procurement tools effectively is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions.
Procurement might seem straightforward—define your needs, pick your vendors, order, track, review, and repeat. However, it can quickly become complex. Strategic sourcing and vendor selection are critical to an organization’s purchasing and growth strategy.
To succeed, you must follow the right steps and use the correct documents. RFI, RFP, and RFQ are more than procurement jargon; they are key tools that streamline your vendor selection, improve project management, and significantly contribute to your procurement success.
The Importance of Strategic Sourcing
The sourcing process is crucial in procurement, aiding organizations in finding potential suppliers that meet their needs and evaluating their capabilities.
Issuing an RFI allows buyers to collect vital information about vendors’ offerings and capabilities, setting the stage for a more focused selection process.
RFQs and RFPs further narrow the vendor selection by focusing on pricing and detailed proposals. These documents help buyers compare features, functionality, and prices across vendors. This ensures they make informed decisions that meet their procurement goals and budget.
8 Key Steps in the Procurement Lifecycle
To streamline the procurement process and achieve successful outcomes, organizations should follow these key steps:
- Identify the need for goods or services and define specifications
- Conduct market research and issue an RFI to gather information about potential suppliers
- Shortlist potential vendors based on their capabilities and offerings
- Issue an RFQ to obtain competitive bids and pricing details from shortlisted vendors
- Evaluate bids and select the most suitable vendor based on predefined evaluation criteria
- Issue an RFP for complex procurement needs, requiring detailed proposals from selected vendors
- Negotiate terms, finalize contracts, and establish a strong buyer-vendor relationship
- Monitor vendor performance, track deliverables, and maintain open communication
Organizations can optimize their procurement process by following these steps and effectively using RFI, RFQ, and RFP documents. This reduces risks and fosters successful partnerships with their chosen vendors.
Request for Information (RFI)
A Request for Information (RFI) allows organizations to gather essential details from potential suppliers. It helps understand a supplier’s offerings, aiding in decisions for complex projects and sourcing. This process also provides procurement with the opportunity to generate strategic advantage.
Purpose and Benefits of RFIs
RFIs serve as a gateway to understanding the market and identifying potential suppliers before delving into the detailed RFP process. They enable you to:
- Gather general information about available products or services
- Identify potential suppliers for your project
- Assess suppliers’ capabilities and experience
- Determine if a supplier can meet your specific requirements
- Narrow down your list of potential suppliers for the RFP stage
5 Key Elements of an Effective RFI
For an effective RFI, include the following elements:
- Company background and qualifications
- Product or service descriptions and capabilities
- Pricing information or cost estimates
- References and case studies
- Include any specific requirements or questions relevant to your project
Best Practices for Issuing RFIs
When issuing an RFI, follow these best practices:
- Be clear and concise in your RFI questions and requirements
- Provide a reasonable timeline for suppliers to respond
- Ensure all potential suppliers receive the same information
- Evaluate RFI responses objectively, focusing on critical criteria
- Use RFI responses to create a shortlist of suppliers for the RFP stage
Incorporating RFIs into your procurement strategy allows you to collect valuable insights. This facilitates informed decisions and enhances sourcing efficiency. It ultimately results in more successful partnerships and better outcomes for complex projects.
Request for Quotation (RFQ)
A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is a formal document buyers use to gather detailed proposals from potential vendors. Its main goal is to standardize the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare and evaluate vendor responses uniformly. By employing a well-designed RFQ template, buyers can elevate their sourcing efforts and make informed decisions that meet their specific needs.
RFQs are commonly employed for direct spend, such as the procurement of specific products like hardware, office supplies, or materials.
These requests focus mainly on cost-related inquiries. This includes questions about cost per unit, bulk discounts, pricing packages, service fees, and delivery terms. When cost is the primary consideration in procurement, an RFQ is the preferred method.
There are four primary types of RFQs:
- Open Bid: Encourages competition among vendors by allowing real-time adjustments to bids based on competitors’ pricing.
- Sealed Bid: Keeps vendor responses confidential until all submissions are in.
- Invited Bid: This method limits vendors to those specifically chosen by the buyer, often to work with known and trusted suppliers.
- Reverse Auction: This method encourages vendors to submit their lowest bids in a competitive setting, typically awarding contracts to the lowest bidder.
Thorough preparation is essential before issuing an RFQ.
This involves working with internal stakeholders to define precise needs and choose the most suitable RFQ type. A well-prepared RFQ should include essential documents, including an invitation to bid, RFQ timeline, business overview, pre-qualification requirements, pricing template, selection criteria, and RFQ scoring guidelines.
Effectively using RFQs in your supply chain management can streamline the procurement process. It ensures transparency and helps identify the best value propositions among competing suppliers.
Investing time crafting a comprehensive RFQ leads to cost savings, improved vendor relationships, and enhanced procurement efficiency.
Request for Proposal (RFP)
A Request for Proposal (RFP) is a detailed document that outlines the buyer’s needs, specifications, and how they will evaluate proposals for a project or purchase.
RFPs are used when the procurement process requires suppliers to provide detailed proposals. These proposals include technical solutions, pricing, and other relevant information.
Unlike RFIs and RFQs, RFPs are more detailed and involve a formal evaluation process to assess proposals against specific criteria.
When to Use RFPs in Procurement
RFPs are often used for complex, specialized projects that require a deep understanding of the supplier’s capabilities and solutions.
For example, in manufacturing, RFPs cover various aspects like packaging, transportation, and freight.
By using RFPs in strategic sourcing, organizations can evaluate suppliers based on their abilities, proposed solutions, and overall fit for the project. This ensures the best project outcome.
Essential Components of an RFP
A well-crafted RFP includes 5 key elements:
- Scope of Work (SOW): A detailed project description, including objectives, deliverables, and timeline.
- Pricing information: A request for a comprehensive price quote, including any applicable discounts or value-added services.
- Contract terms and conditions: The legal framework governing the relationship between the buyer and the supplier, including payment terms, warranties, and intellectual property rights.
- Evaluation criteria: The factors and weightings used to assess supplier proposals, such as technical expertise, past performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- Reference information: A request for relevant case studies, testimonials, or references demonstrating the supplier’s experience and success in similar projects.
Evaluating RFP Responses
After receiving RFP responses, the buyer must evaluate each proposal to find the best fit for their needs. This process may involve using an evaluation tool, like a weighted factor matrix, to assess products or services based on specific criteria.
Buyers can identify the supplier with the best technical expertise, quality, and value by thoroughly evaluating proposals in the purchasing process. This can lead to a successful partnership and project outcome.
Effective communication and negotiation skills are crucial throughout the RFP process. They ensure all parties understand the project requirements, expectations, and deliverables.
By following best practices and leveraging RFPs, organizations can streamline their procurement processes, secure the most suitable suppliers, and drive long-term success in their purchasing endeavors.
Key Differences Between RFI, RFQ, and RFP
Understanding the distinctions between RFI, RFQ, and RFP is crucial in procurement. Each document has a unique purpose and is utilized at different procurement stages. Recognizing these differences aids in streamlining sourcing, reducing costs, and managing risks in supplier selection.
Purpose and Timing of Each Document
RFIs are used early in procurement to gather market insights, assess supplier capabilities, and identify potential vendors. This non-binding document helps narrow down a list of qualified suppliers for further evaluation.
RFQs are employed when requirements are clear, focusing on competitive pricing from suppliers. This more structured document often needs technical input for complex products or services.
RFPs are the most detailed and are used for high-value, strategic purchases. The RFP process can span several months to over a year and evaluates supplier proposals against set criteria.
RFPs cover the scope of work, pricing, contract terms, and evaluation tools.
Level of Detail and Specificity Required
RFIs are less structured and may have a length limit, so verifying requirements before submission is essential.
When responding to RFIs, use an active voice and customer terminology and support claims with relevant documentation.
RFQs require more detail, especially on pricing and technical specifications. Suppliers must offer accurate, competitive pricing to progress in the procurement process. Technical input from solutions architects may be necessary for response accuracy.
RFPs demand the most detail and specificity. Suppliers must provide comprehensive proposals covering technical capabilities, implementation plans, risk management strategies, and pricing. To stand out in the bidding process, a well-organized response with a strong introduction and summary is important.
Understanding the differences between RFI, RFQ, and RFP optimizes procurement, leveraging the right tools and methodologies for data-driven decisions. Effective management of these documents leads to cost savings, improved supplier relationships, and a more agile procurement function.
Best Practices for Streamlining Procurement with RFx Documents
Enhancing your procurement process can significantly boost your organization’s efficiency and effectiveness. By using standardized templates and technology, you can streamline your RFx management, leading to better outcomes and strategic sourcing decisions.
Standardizing RFx Templates
Standardizing your RFI, RFQ, and RFP templates can significantly reduce the time spent on procurement initiatives. It ensures consistency across processes.
With a standardized format, you can gather comparable information from potential vendors, making evaluating and comparing their offerings easier.
This approach also minimizes confusion among suppliers as they become familiar with your organization’s standardized questionnaires and requirements. When creating standardized templates, consider including essential elements such as clear instructions, detailed specifications, evaluation criteria, and submission deadlines.
Collaborating with cross-functional teams, including experts from manufacturing, transport, and legal departments, can help ensure your templates cover all necessary aspects. They should align with your organization’s policies and objectives.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient RFx Management
Technology solutions like RFx software can significantly streamline your procurement process. These tools provide a structured framework for issuing and managing RFPs, RFIs, and RFQs. They eliminate manual bottlenecks and enhance collaboration among stakeholders.
By automating tasks such as document creation, distribution, and vendor scoring, you can save time, allowing you to focus on more strategic aspects of procurement.
When selecting an RFx software, look for features that support your specific needs, such as:
- AI-powered document creation to ensure consistency and reduce errors
- Intelligent vendor matching to engage with the most suitable suppliers
- Automated document distribution and response collection for efficient communication
- AI-driven vendor scoring for fair and transparent decision-making
In addition to leveraging technology, providing training and development opportunities for your procurement team is crucial.
By enhancing their knowledge of RFx processes and technological tools, you can empower them to manage vendor relationships effectively. This drives continuous improvement in your procurement practices.
RFI, RFP, RFQ in Procurement Orchestration
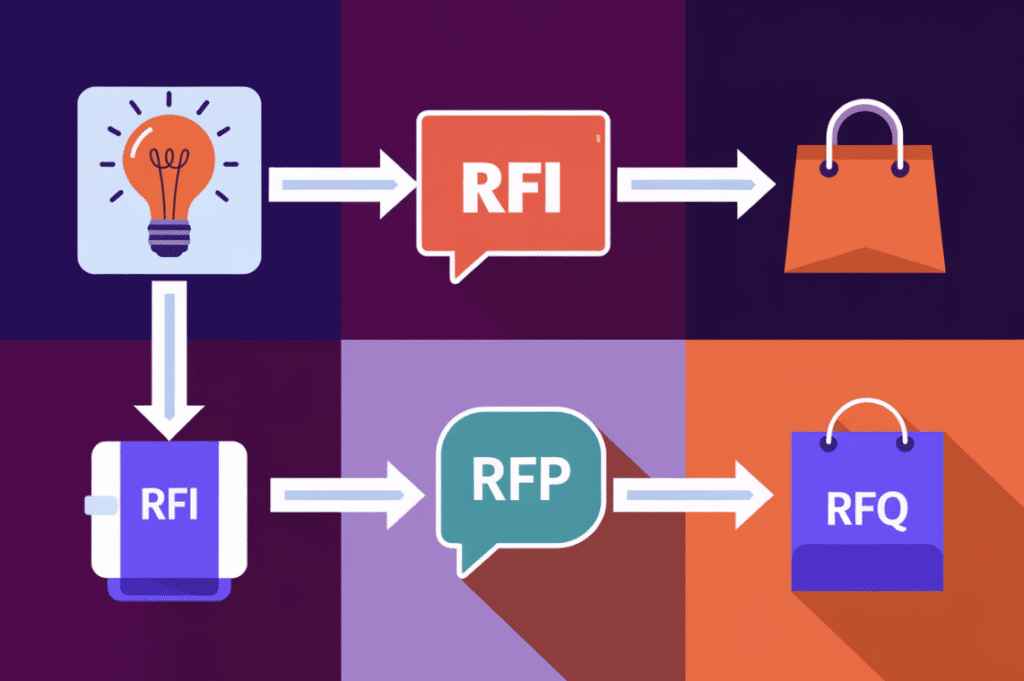
Procurement orchestration is a strategic method that simplifies the procure-to-pay process, from sourcing to payment. It uses technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence to improve supplier management, increase transparency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The RFx documents, including Request for Information (RFI), Request for Proposal (RFP), and Request for Quotation (RFQ), are essential in procurement orchestration. They help organizations make informed decisions and reach their goals.
The Role of RFx Documents in Procurement Orchestration
RFx documents are vital for effective procurement orchestration. They collect crucial information, evaluate potential suppliers, and pick the best vendor for the job. With RFx documents, procurement teams can:
- Define project scope and specifications
- Communicate their needs and expectations to suppliers
- Assess supplier capabilities and expertise
- Compare and evaluate supplier offerings
- Negotiate terms and conditions
- Make data-driven sourcing decisions
Integrating RFx Processes with Procurement Software
Organizations are now integrating RFx processes with advanced procurement software to enhance their benefits. This automation and standardization of RFx workflows allows procurement teams to:
- Streamline the creation, distribution, and management of RFx documents
- Collaborate effectively with internal stakeholders and suppliers
- Ensure compliance with organizational policies and regulatory requirements
- Leverage pre-built templates and libraries to save time and effort
- Conduct comprehensive supplier evaluations using customizable scoring criteria
- Gain real-time visibility into the status of RFx processes
Achieving End-to-End Visibility and Control
Procurement orchestration, powered by RFx documents and software, gives organizations full visibility and control over their sourcing. By centralizing data, automating workflows, and using advanced analytics, procurement teams can:
- Monitor supplier performance and compliance
- Identify potential risks and opportunities
- Optimize spend and maximize cost savings
- Improve supplier relationship management
- Drive continuous improvement and innovation
- Demonstrate the value and return on investment of procurement initiatives
About 35% of enterprise procurement teams are using AI for procurement, so systematically integrating RFx documents with procurement orchestration is becoming crucial.
Common Challenges and Solutions in RFx Management
Managing RFx processes, including RFIs, RFPs, and RFQs, is complex and time-intensive for procurement teams. Despite their strategic benefits, these documents often face challenges that affect procurement efficiency and effectiveness. Organizations struggle with these issues, making their operations less streamlined.
One major issue is the lack of standardization in RFx templates. This inconsistency confuses vendors, making it hard for them to respond accurately. Comparing vendor responses becomes a challenge without a uniform structure.
Another significant challenge is the manual nature of RFx management. Procurement teams spend hours on creating, distributing, and evaluating RFx documents. This manual effort leads to delays and increased costs. It also raises the risk of errors and inconsistencies in vendor data.
Procurement teams should adopt best practices and use technology to overcome these challenges. Some solutions include:
- Standardizing RFx templates for consistency and easy comparison
- Using Focal Point procurement software to automate the creation, distribution, and evaluation of RFx documents
- Integrating RFx processes with procurement systems for end-to-end visibility and control
- Providing training and support to procurement staff for effective RFx management
By addressing these common challenges and implementing these practical solutions, organizations can improve their RFx management processes. This reduces manual tasks, improves procurement efficiency, and improves overall value. It also fosters better vendor relationships and cost savings.
In Summary
RFI, RFP, and RFQ are vital for procurement, helping organizations streamline their sourcing. These tools allow procurement teams to evaluate suppliers thoroughly, make informed decisions, and enhance business value. To excel in strategic sourcing and remain competitive, it’s essential to grasp the differences between RFI, RFP, and RFP.
Improving the efficiency of sourcing initiatives involves adopting best practices for procurement documents. Standardizing RFx templates and using AI in procurement software can streamline the process, providing end-to-end visibility and control over procurement activities.
Understanding the distinctions between RFI, RFQ, and RFP can help procurement teams more effectively manage supplier evaluation and selection.
Effective procurement is key for organizations aiming to boost financial performance, competitiveness, and sustainability. Leveraging RFI, RFP, and RFQ in procurement orchestration helps identify the best suppliers and negotiate favorable terms. Integrating these tools into your procurement strategy ensures long-term success in a dynamic market.